In FY2023, the Oji Group's total water intake was 695 million m3, total wastewater discharge was 672 million m3, and water consumption was 23 million m3. The Oji Paper Group is working to make effective utilization of water resources with the goal of reducing the water intake intensity of the Group as a whole by 6% or more in FY2030, compared with FY2018. Oji Paper, Oji Materia, Oji F-tex, and Oji Nepia, which water intake accounts for approximately 80% of total water intake, have formulated specific reduction plans for 2030 and are working on them. The secretariat of the Sustainability Committee receives quarterly reports on reduction performance from each company and reports to the directors twice a year at the Sustainability Committee.
| FY2018 | FY2019 | FY2020 | FY2021 | FY2022 | FY2023 | Compared to FY2018 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water intake (million m3) | 740 | 737 | 706 | 714 | 710 | 695 | - |
| Water intake intensity (1,000 m3/million yen) | 0.48 | 0.49 | 0.52 | 0.49 | 0.42 | 0.41 | -14.2% |
| Waste water (million m3) | 708 | 701 | 672 | 676 | 673 | 672 | - |
| Water consumption (million m3) | 32 | 36 | 34 | 38 | 37 | 23 | - |
Water used at the plant is not only surface water from rivers and other sources, but also groundwater and third-party water sources (industrial water, etc.) to diversify risks.
| FY2018 | FY2019 | FY2020 | FY2021 | FY2022 | FY2023 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Surface water (river, lake, etc.) (million m3) | 488 | 483 | 463 | 466 | 453 | 443 |
| Surface water (sea) (million m3) | 10 | 10 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 9 |
| Groundwater (million m3) | 137 | 133 | 128 | 127 | 131 | 128 |
| Third party organization (million m3) | 106 | 111 | 106 | 112 | 117 | 115 |
All of the Group's business sites have formulated water management plans to control water intake, wastewater discharge, and the quality and temperature of water at the time of discharge. In addition, the Group is taking steps, including water reduction, to make effective use of water resources and reduce environmental impact. In addition, the Corporate Sustainability Department collects environmental data (water intake, wastewater discharge, etc.) and examples of water conservation measures from all business sites every year, and horizontally disseminates effective measures to each business site.
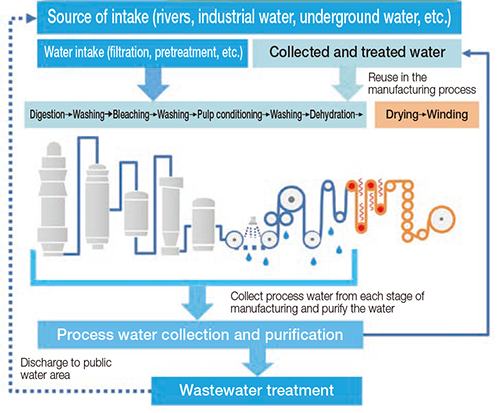
Paper and paperboard mills use a large amount of water throughout the entire production process, including pulp evaporation, washing, bleaching, conditioning, and papermaking. However, water from each process is collected, treated, purified, and reused (recycled). In addition, water used in the final stage of the papermaking process, drying (steam drying), is also recovered and reused.
The World Resources Institute's (WRI) AQUEDUCT water risk assessment tool uses the Water Risk Baseline Water Stress indicator to rate the degree of potential conflict with other users of water on a 5-point scale (Extremely High, High, Medium to High, Low to Medium, Low or No data). The higher the rating, the more competition and the higher the risk. https://www.wri.org/aqueduct
Oji Holdings Group companies refer to the above AQUEDUCT assessment and implement risk reduction initiatives at each business site. The following are representative examples.
IPI joined the group in FY2023. Immediately after joining the group, IPI upgraded its boiler cooling tower and installed RO membrane treatment equipment. This enabled IPI to reduce the amount of chloride ions in wastewater generated during the softening process of water (hard water) used for production, while at the same time reducing the amount of water consumption.
Jiangsu Oji Paper has significantly reduced water consumption by implementing the "best available technology" recommended by the European Commission for environmental protection purposes in paper and pulp production.
Oji Materia Osaka Mill has adopted and implemented the following techniques, which are among the "best available techniques". As a result, we have reduced the water intensity (m3/ton), which represents the amount of water used (m3) relative to the amount of paperboard produced (tons), to the single-digit range, and are proud of our industry-leading high water usage efficiency.
For more technical information, see [Best Available Techniques (BAT) Reference Document for the Production of Pulp, Paper and Board (europa.eu)]
CENIBRA is recovering cooling water for effective use as water, and in the future, as part of the plant's modernization project, CENIBRA will invest in equipment to increase heat recovery efficiency, which is expected to further reduce water consumption by optimizing steam.
New installation of water treatment facilities that enable recycling of previously unused wastewater generated in various manufacturing processes and other measures.
Oji Paper and Oji Materia mills are working to purify wastewater by implementing the advanced treatment of wastewater recommended in the "Best Available Technologies" section above (BAT.7.3.12, based on BAT, tertiary treatment of wastewater) and setting voluntary control values that are even stricter than the effluent regulation values.
As noted above, IPI changed from ion exchange resins to RO membrane treatment facilities in the softening treatment of water (hard water) used in production. This change has resulted in the purification of wastewater by reducing the generation of chloride ions in the wastewater.
The total amount of expenses and investments required for wastewater treatment and other water-related activities in FY2023 were 7,834 million yen and 797 million yen, respectively.
With regard to wastewater treatment, the Group has begun to develop advanced wastewater treatment technology utilizing remote monitoring and AI in order to improve and stabilize treated water quality and optimize operating costs and operational management, which is expected to contribute in the future.
Wastewater generated by Jiangsu Oji Paper through manufacturing processes is treated and purified until it meets the regulatory levels for wastewater, then transferred to Nantong Nengda Water Co., Ltd. in Nantong Economic & Technological Development Zone. After undergoing various treatment processes, this water is all used as recycled water within the Economic & Technological Development Zone.
Recycied water is water of a quality between tap water and sewage,and is used for industrial purposes.

The depletion of water resources and damage from floods caused by climate change in recent years pose significant risks not only to the continuity of businesses but also to industries and people’s health in the communities where businesses operate. To better understand the water risks involved in its business operations, the Oji Group refers to assessments made by the World Resources Institute (WRI), a global environmental research organization.
An analysis of water risk at all 308 business sites was carried out using the WRI’s AQUEDUCT water risk assessment tool. The results showed that there were 21 sites located in areas with high water risk (Baseline Water Stress: High and Extremely High). Fact-finding surveys were conducted of these 21 highrisk business sites to investigate the actual water risks and their financial impacts.
As a result, in terms of total water intake and water consumption, these high-risk sites accounted for less than 1% and 2% of the Group, respectively, and for 2% of total production. To analyze the potential financial impact of water risks, we also considered scenarios in which these facilities were forced to suspend operations due to water shortages. However, as the sales and assets of these sites account for only about 4% of the Group’s total, the financial impact was consequently estimated to be low.
Additionally, in order to mitigate water-related risks, we are currently investing approximately 30million yen per year in the development of water treatment technology as a research theme. In the future, this may contribute to the stability and growth of the entire group by mitigating water risks and developing new water-related businesses.
| FY2023 | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of business sites*2 | Water intake (Thousands of m3) |
Water consumption (Thousands of m3)*3 |
Production volume (Thousands of tons) |
Sales Revenue (¥billion) |
Assets (¥billion) |
||||||
| Low (<10%) or No data | 70 | 342,312 | 49% | 7,908 | 35% | 6,594 | 44% | ||||
| Low to medium (10-20%) | 122 | 215,140 | 31% | 4,529 | 20% | 4,484 | 30% | ||||
| Medium to high (20-40%) | 95 | 135,898 | 20% | 9,754 | 43% | 3,607 | 24% | ||||
| High (40-80%) | 4 | 1,254 | 0% | 266 | 1% | 103 | 1% | 71.6*4 | 4% | 90.8*4 | 4% |
| Extremely high (>80%) | 17 | 217 | 0% | 88 | 0% | 209 | 1% | ||||
| Total | 308 | 694,820 | 100% | 22,545 | 100% | 14,998 | 100% | 1,696.3*5 | 100% | 2,442.5*5 | 100% |
For those business sites evaluated as high risk, we conduct annual interviews to ascertain the impact of water shortages and flooding on operations, the frequency of their occurrence, and to hear examples of the countermeasures being implemented.
The results of the interviews conducted in fiscal 2023 showed that no issues with production or operations were identified at any business site, and no potential water risks were observed.
However, business sites reported proactive environmental protection actions, such as implementing voluntary initiatives to reduce water usage, engaging with stakeholders to reduce water consumption, and participating in water resource conservation activities led by public institutions.
| Water risk assessment | country | Number of Business Sites | Impact on Operations Due to Water Shortage | Impact on Operations Due to Flooding | Measures to Reduce Water Risk | Activities in Collaboration with Local Governments, Related Organizations, and Supply Chain |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Extremely High | China | 6 | None | None |
|
- |
| India | 5 | None | None |
|
|
|
| Thailand | 4 | None | None |
|
|
|
| Italy | 2 | None in the past 10 years | None in the past 10 years |
|
- | |
| High | Indonesia | 2 | None in the past 10 years | None in the past 10 years | - |
|
| Germany | 1 | None | None |
|
|
|
| Australia | 1 | None | None |
|
- |
The 21 business sites either treat their wastewater or use wastewater treatment facilities owned by the industrial park under contract, monitor the amount of wastewater and substances of concern in the wastewater, and report regularly to the local government and water resource management agencies.
Furthermore, 21 business sites are subject to environmental audits by the Oji Group, and there have been no cases of legal violations or serious accidents. For details, please refer to "Promotion of environmental compliance".
As a result, we confirmed that all business sites initially assessed as high risk in the risk evaluation are currently considered to be low risk.
Water resources, along with forests and biodiversity, are resources shared by the community, and sustainable resource use is desirable. In particular, production sites actively engage in dialogue with local stakeholders on water use, water conservation, and water resource conservation concerning water resources that are essential for production.
CENIBRA, Brazil: CENIBRA as a representative of the private sector, participates in local river basin committees and forest dialogue councils, contributing to the development of the forest sector and strategies for the conservation of water resources, natural resources, and biodiversity.
KANZAN (One of the initiatives at the water risk site), Germany: WVER is in charge of water resources management and wastewater treatment in Düren, Germany, where KANZAN is located. The association is a public organization with the participation and management of residents and companies in the area. In addition to providing a stable water supply and wastewater treatment in the area, the association's role is to conserve water resources, and KANZAN attends meetings and participates in activities as a member.
Oji Paper Tomioka Mill and Yonago Mill participate in the Naka River South Bank Land Improvement District Water Use Association, etc. and the Hino River Basin Water Use Council, respectively, and are working to reduce water intake in accordance with dam storage rates in order to prioritize the use of local agricultural water during summer water shortages.
Oji F-Tex Shibakawa Mill has signed a memorandum of understanding regarding water use with the local Fisheries Cooperative and cooperates in protecting the local environment and aquatic life.
CENIBRA's eucalyptus plantations and pulp production use water from the Doce River basin in the region. In recent years, there has been less rainfall than usual, and the risk of a water shortage has been a concern for the entire region. To address this issue, CENIBRA has identified the sub-basins of greatest influence based on regular water monitoring at each water point. In collaboration with public authorities and local residents, CENIBRA is focusing on water conservation activities for these sub-basins to improve their practices on access to water and sanitation. Specifically, CENIBRA is working on the following initiatives:
Since 2018, CENIBRA has built 100 reservoirs in its forests, storing a total of more than 1 million m3 of water, allowing excess water during the rainy season to slowly percolate into the soil, later into the river, maintaining the level of the water table in the basins. The location of these reservoirs was determined considering the water supply for residential use, increasing harmony with the local communities regarding the use of water resources.

In recent years CENIBRA has developed subsoiling activities prior to planting seedlings to improve the regular infiltration of rainwater into the soil compacted by the activity of heavy machinery in its own forests. Now CENIBRA is transferring this technique and expertise to its neighbors, including log suppliers and farmers, who are contributing to the recovery of underground water retention in compacted pasture lands, as well as the prevention of erosion resulting in better water quality in the basin.

Within the scope of the Spring Protection Project, CENIBRA has played a crucial role in preserving springs located on third-party lands, especially those used for livestock and related activities. These areas, recognized as Permanent Preservation Areas under the Brazilian Forest Code, require landowners to ensure the preservation of native vegetation within them. However, many rural producers in the region were unaware of proper protection methods or faced economic constraints, resulting in inadequate conservation practices.
In this context, CENIBRA took the initiative to identify the basin of the Rio Doce tributary as a priority area for water source protection, promoting actions that encourage producers to protect springs. This included providing materials, adopting technologies, and installing protective fences. The delineation of these areas prevents the entry of livestock, which previously had free access, avoiding water source contamination and allowing for natural vegetation regeneration.
Between 2017 and 2023, over 1,300 hectares of Permanent Preservation Areas, including all springs supplying the municipality of Peçanha, were effectively protected. In addition to the positive environmental impact, this project also significantly contributed to raising awareness among landowners about the importance of water resources and biodiversity conservation. This partnership between CENIBRA, the municipality of Peçanha, and the local community strengthens ties and promotes mutual engagement towards sustainability and collective well-being.
