The Oji Group announced its support for the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD) in December 2020 and is working on the climate-related information disclosure recommended by the TCFD.

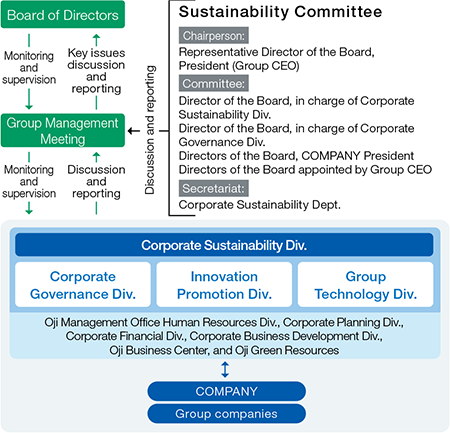
Recognizing efforts for sustainability including addressing climate change issues as one of the important management challenges, the Oji Group established the Sustainability Committee and the Corporate Sustainability Division in April 2022. We deliberate matters that are material to fulfilling our commitment to sustainability through the Sustainability Committee and monitored and supervised by our Board of Directors.
The Sustainability Committee, chaired by the Representative Director of the Board, President of Oji Holdings Corporation (Group CEO), who is responsible for overall sustainability including climate change, and consisting of Directors of Oji Holdings Corporation (including Presidents of all COMPANIES and female outside directors), discusses the Group’s risks associated with sustainability and measures against those risks biannually. Matters discussed at the Committee are referred for discussion and reported to the Group Management Meeting depending on the importance, and after deliberation by the Meeting, the Board of Directors makes a decision on execution of matters. In FY2023, revisions to the Human Rights Policy and the Environmental Action Program 2030 were decided.
The Corporate Sustainability Division, which integrates the Group's sustainability management, identifies climate-related risks and opportunities across the Group. In order to properly manage these risks and opportunities, the division disseminates them throughout the Group, and reports monthly to the responsible division director and twice a year to the Group Management Meeting. Significant risks and opportunities are reported to the Board of Directors based on the judgment of the division director. In addition, as the secretariat of the Sustainability Committee, the Corporate Sustainability Division carries forward mattersdetermined by the Committee.
Climate-related risks and opportunities for us have been analyzed as shown below. We recognize the importance of transition risks due to policies and regulations such as carbon taxes in the medium term toward 2030, physical risks such as changes in precipitation and weather patterns in the long term toward 2050, and opportunities for increased demand for low-carbon products in the medium to long term.
To meet challenges for transition to a decarbonized society, we have set our GHG emissions reduction targets and are working to reduce coal consumption, increase the net increment in carbon stocks by forests, and develop wood-derived products as a plastic alternative. While continuing our present efforts to curb the negative impact on our business from the transition to a decarbonized society, we will continue to analyze risks and strengthen our resilience*1.
The Corporate Sustainability Division examines risks on a Group wide basis with assistance from external experts, and the Sustainability Committee analyzes them while discussing their importance and priority. Impacts on our business, strategy, and finances are assessed quantitatively and qualitatively, using scenarios for 1.5℃ (2℃) and 4℃ for the medium term (2030) and the long term (2050)*2.
The Corporate Sustainability Division is in charge of overall management of responses to climate-related risks based on the strategy across the Group, and the Sustainability Committee manages the progress. Specifically, for the reduction of GHG emissions, we have organized a project team and are working to reduce coal consumption and expand the net increment in carbon stocks by forests. Furthermore, climate-related risks are referred for discussion and reported to the Group Management Meeting depending on the importance, and integrated into company-wide risk management.
We have set the following targets based on the 1.5℃ target in the Paris Agreement. The carbon price of 140 USD/t-CO2 (2030 level in developed countries) from the Net Zero Emissions (NZE) scenario of the International Energy Agency (IEA) is used as the internal carbon pricing (ICP) for risk analysis and evaluation items for investment decisions.



| Type | Driver (Factor causing an impact on our business) |
Awareness of business environment | Impact on our business | Strategies and countermeasures | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.5℃ (2℃) scenario | 4℃ scenario | |||||||
| 2030 | 2050 | 2030 | 2050 | |||||
| Transition risks | Policies, laws and regulations | Fluctuation of fossil fuel-derived energy prices | Increase in costs related to procurement using fossil fuel-derived energy and electricity due to changing energy mix | Small | Small | Small | Small |
|
| Tightened CO2 emissions regulations | Increase in energy consumption and credit operating costs due to the Enhance the operation of renewable energy sources such as hydro and biomass energy toward net zero carbon emissions in FY2050 introduction of carbon tax and tightening of regulations on emissions trading | Large* | Small* | Medium* | Small* | |||
| Markets | Increasing stakeholders’ interest in low-carbon products and services | Increase in boycott activities toward products and services created using energy derived from fossil fuels due to increased awareness of decarbonization among consumers | Small | Small | Small | Small |
|
|
| Reputation | Negative feedback from stakeholders |
|
Medium | Medium | Small | Small |
|
|
| Physical risks | Acute | Increasing severity of extreme weather events | Business stagnation such as facilities affected by and supply chain disruptions caused by a large scale natural disaster | Small | Small | Small | Small |
|
| Chronic | Changes in precipitation and weather patterns, and rising average temperatures | Increase in procurement costs primarily as a result of deterioration of growth conditions for trees, key raw materials for our products | Small | Small | Large | Large |
|
|
| Opportunities | Resource efficiency | Effective resource utilization Reduction in water use and consumption |
Increase in demand for advanced water treatment technology and water management due to flooding, drought, precipitation fluctuations, and higher demand for clean water in water stress areas | Small | Small | Medium | Medium |
|
| Energy sources | Use of low emission sources of energy | Increase in demand for renewable energy toward realization of a decarbonized society | Small | Medium | Small | Small |
|
|
| Products and services |
|
Increase in demand for low-carbon and environmentally-friendly products due to increased awareness of decarbonization and environment | Large* | Large* | Large* | Large* |
|
|
| Markets | Use of incentives |
|
Small | Medium | Small | Small |
|
|